Theme: A step towards advancements in the research, treatment and eradication of Infectious Diseases
Bacterial Diseases 2019
ME Conferences invites all the Nobel laureates, speakers, delegates, microbiologist from all over the world to attend Annual Conference on Bacterial, Viral and Infectious Diseases during June 17-18, 2019 in Dubai, UAE. The theme of the conference is “A step towards advancements in the research, treatment and eradication of infectious diseases". These conferences prompt keynote presentations, Oral talks, Poster presentations and Exhibitions.
Bacterial diseases 2019 is a global platform for researches that afford a new discovery into microbiology, Clinical diagnostics of Bacterial, Viral and Infectious diseases. It also provides a platform to discuss on latest diseases on bacteria and virus. Bacterial Diseases meeting 2019 is hosting presentation of prominent journals and discussion on Bacteriology and Virology. The Organising Committee Member can also invite the young researchers to summit their latest scientific researches for poster session.
Bacterial diseases congress 2019 will provide an international platform for discussion and representing their views on present and future challenges in various infectious diseases, latest diagnosis methods and modern treatments. It gives an opportunities to the young to represent their thought regarding the forensic bacteriology, forensic virology and the techniques regarding this.
ME Conferences organize a series of 3000+ Global Events inclusive of 1000+ Conferences, 500+ Upcoming and Previous Symposiums and Workshops in USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific societies and publishes 700+ Open access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Target Audience
- Bacteriology Students and Scientists
- Virology Students and Scientists
- Bacteriology Faculties
- Virology Faculties
- Microbiologist
- Medical Colleges
- Researches Laboratories
- Virology Researchers
- Bacteriology Researchers
- Centre for Global Research and Intervention in Infectious Diseases
- Non-Government Organisations
- Dean and Directors
- Graduates and Undergraduates
- Pharmaceutical Industries
- Healthcare Sectors
- Directors of Association and Society
- Experts and Delegates
- Doctors
- Research Institutes
- Industrial Business Entrepreneurs
Conference Highlights
- Bacteriology
- Virology
- Clinical Aspects of Bacterial infection
- Clinical Aspects of Virus
- Epidemiology
- Pathogenesis
- Animal Bacteriology
- Human bacteriology
- Plant bacteriology
- Animal virology
- Agriculture and Plant virology
- Human virology
- Pediatric viral diseases
- Medical virology
- Molecular biology research and viral therapy
Track 1: Bacteriology
Bacteria are single cellular microorganisms that lack a nuclear membrane and are dividing by binary fission. The study of bacteria called as bacteriology. Bacteriological study helps in the field of agricultural, or soil, bacteriology; clinical diagnostic bacteriology; industrial bacteriology; marine bacteriology; public-health bacteriology; sanitary, or hygienic, bacteriology; and systematic bacteriology. Major researches in this field help in development of many useful vaccines. The major advantages are the discovery of antibiotics that are helpful in the diagnosis of various types of disease. Recombinant bacteria are useful in bacteriologic research to manufacture biomolecules (e.g. interferon) needed for research and patient care.The human gut microbiome creates over early adolescence and helps in sustenance absorption and immunomodulation, yet the systems driving its improvement stay subtle.
Track 2: Virology
Virology is the study of viruses, about the nucleic acid and protein that are responsible for their replication in plants, animals, and humans. It reveals about the study of their distribution, biochemistry, about their histology, ecology and clinical aspects of the virus. It is the scientific discipline concerned with the viruses, physiology, molecular biology and viral diseases along with their causal agents. Cells affected by viruses and the changes in its in response to the virus lead to the manifestations of the viral disease. Characteristic based arrangement balances out after the principal year, while ordered turnover proceeds unabated
Track 3: Global Spread of Viruses
The distribution of viruses and viral infections across the world is referred to as epidemiology. Most epidemiologic studies of infectious diseases have targeted the factors that influence the acquisition and spread because this knowledge is important for developing methods of prevention and control. Historically, epidemiologic studies and the application of the knowledge gained from them have been central to the control of the great epidemic diseases, like cholera, plague, smallpox, yellow fever, and typhus.The previous 500 years have given various instances of how the foundation and development of overall transport systems has encouraged worldwide pandemics of transmittable sicknes
Track 4: Parasitology and Pediatrics
Parasitology is that the study of parasites, their hosts, and also the relationship between them. Parasitology is the science overseeing parasites that sully man, inflicting contamination and ill-being in many countries of the tropics. As a biological discipline, the scope of parasitology is not determined by the organism or setting in question, but by their approach of life. There are specific types of parasites and hosts. They torment billions of individuals, kill millions consistently, and convey devastating injuries, for example, visual disability and disfiguration on additional millions. World Health Organization surveys that one individual in every four harbors parasitic worms.Restorative Parasitology is the part of sciences managing parasites which taint people, the maladies brought about by them
Track 5: Neglected Tropical and Rare Infectious Diseases
Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs) are a major public health problem globally. These are the Diseases that are galore in tropical Region and primarily affecting the world’s poorest population and largely within the developing countries. As they affect poor people they continue to be unnoted, therefore are referred to as “Neglected”. These diseases doesn't include the major three Infectious i.e. AIDS, tuberculosis, Malaria. Rare Diseases refer to those medical aberrations that have an effect on a very least number of the population. they're characterized by a wide diversity of disorders and symptoms that differs not only from disease to disease however conjointly from individual to an individual patient suffering from the same disease.The generally realized pathogens incorporate infection, microscopic organisms, growths or parasites
Track 6: Infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases is a sickness caused by organism like microorganism, viruses, fungi or parasites into human beings and also plants and animals. Most of the infectious diseases are usually passed from one person to a different person, and some of the infectious diseases are transmitted by bites from insects or animals, and a few are obtained by contamination of food or by water or by being exposed to organisms that are part of nature.hello torment billions of people, murder millions reliably, and pass on pulverizing wounds, for instance, visual incapacity and disfiguration on extra millions
Track 7: Clinical Microbiology and Virology
Clinical microbiology is the branch of microbiology that deals with the study of the molecular basis and any microbes that cause infections. Clinical microbiologists must be able to tell the transformation between normal microorganisms expected in a very specimen and those inflicting an infectious disease.Medicinal microbiology begins with the survey of the insusceptible framework, by which the microorganisms or poisons enter by power so as to vanquish and experience the cells
Track 8: Clinical Immunology
Clinical immunology is a medical subspecialty largely targeted on a specific physiologic process, inflammation, that is essential to good health, notably in defense against pathogenic organisms and recovery from injury. However, inflammation, mediated by the cells and soluble products of the immune system, is also a robust contributor to the pathogenesis of diseases that affect virtually every organ system. Others are biochemical barriers, for example, dissolvable - lysosyme, intense stage reactants and supplement, fibronectin, interferons. Cell segments incorporate common executioner cells, RES phagocytes
Track 9: Infectious Diseases Prevention, Control and Cure
An infectious disease is a major unavoidable fact of life hence infection control does raise as a major concern for the Government especially in a health care and public health practice setting. WHO 100 Core Health Indicators list has clearly mentioned the need for Infection prevention and control (IPC) programmes to be reinforced in all healthcare facilities globally. Public Awareness and Public Health laws are incorporated to prevent and control the transmission of infectious diseases. Aseptic methods, sanitation, disinfection, vaccination, Sterilization, healthy hygiene practices, and early diagnosis do help in preventing and controlling infectious diseases.
Track 10: Pharmacoepidemiology
Over the years, many diseases which were said to be extinct have re-emerged and the re-emergence is not limited to a single population or country. Re-Emerging Infectious Diseases like Ebola, SARS has become a major international public health concern and combating them with Epidemiology studies and International Health regulations has been the goal. The branch of medicine which deals with the study of “how often diseases occur in different groups of people and why” is termed as Pharmaepidemiology. The study focuses on the distribution (who, when, and where) and determinants of health and disease conditions in defined populations. It involves the employment of methods like supervision, monitoring, statistical inference, analytic researches, and experiments.
Track 11: Symptoms and Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases are diseases caused by microorganisms like bacteria, virus, fungi, and parasites. Food contamination, insect bites, direct/ indirect contact with animals, materials or persons can be the factors for harmful pathogens to get in contact with the host and be the causative agent for the disease. The common symptoms include fever, diarrhea and fatigue.
Track 12: Mechanism of Resistance
Instrument of obstruction is a direct result of the inactivation or change in the objective site of the anti-infection that diminishes its coupling limit, to maintain a strategic distance from the anti-toxin impact and the reduced intracellular enemy of microbial social occasion, diminishing porousness or potentially expanding dynamic efflux of the anti-infection. A host can develop two sorts of barrier components to expand its health when tried with a pathogen-obstruction and resistance. It is fundamental to separate between these two resistances components since they have differing epidemiological and obsessive effects. Extended cognizance of these guards could prompt progressively compelling treatment techniques and a superior depiction of host-parasite associations.
Track 13: Antiviral, Antibacterial, Antifungal Agents
AMR-Antimicrobial Resistance has been a major concern among scientists and clinicians worldwide. It is observed that microorganisms like pathogenic viruses, bacteria, fungi, and protozoa have been developing resistance and are more difficult to treat with the existing drugs. To overcome this drawback, several natural and synthetic compounds are discovered, synthesized and tested for their antiviral, antifungal and antibacterial activity. Agents with antiviral/antibacterial/antifungal properties can have a better mode of action against pathogens serving as effective drug and can have a wider market in pharmaceutical industries to treat several infections.
Track 14: Advanced In AntiMicrobials and Vaccines
Vaccination may be a process of administration of an antigenic material (vaccine) into a living mechanism. The clinical effect desired is to cause stimulation of an individual's system so as to develop an adaptive immunity against the pathogen constituting the vaccine. Vaccination is the most effectual method of prevention for infectious diseases. vaccine Adjuvants are components which enhance the immune system and accelerate the immune responses to an antigen. Antimicrobial is the agent that kills or restricts the cell growth. To fight against the potential bacteria nowadays, the manufacturing firms are coming up with a lot of advanced antimicrobial liquids/soaps/sanitizers. Immunization/Vaccination is one amongst the foremost efficient public health interventions thus far, saving millions of lives and protecting countless children from health problem and disability.
Track 15: Case Studies
A case study, explores the biology of different infectious diseases, covering a variety of topics including the virus, infection, replication, mutation, immune responses, pathology, surveillance, diagnosis, and treatment.
Track 16: Vaccination against Bacteria Viral Infections
Inoculation against a scope of bacterial and viral ailments is an essential piece of transferable sickness control around the world. Inoculation against a particular illness not just decreases the frequency of that sickness, it lessens the social and financial weight of the malady on networks. High inoculation inclusion can prompt total hindering of transmission for some immunization preventable ailments (VPDs). The overall destruction of smallpox and the close annihilation of polio from numerous nations give brilliant instances of the job of inoculation in illness control.
Track 17: Cell Death in Cancer and Infectious Diseases
immunogenicity relies upon two key elements: antigenicity and adjuvanticity. The nearness of exogenous or changed antigens clarifies why tainted cells and threatening cells can start a versatile resistant reaction gave that the phones additionally emanate adjuvant flags as a result of cell stress and demise. A few irresistible pathogens have concocted techniques to control cell passing and limit the outflow of risk signals from biting the dust cells, consequently keeping away from safe acknowledgement. Correspondingly, disease cells regularly escape immunosurveillance inferable from deformities in the sub-atomic hardware that underlies the arrival of endogenous adjuvants. Here, we survey current information on the components that underlie the initiation of invulnerable reactions against kicking the bucket cells and their pathophysiological importance.
Bacterial, Viral and Infectious Diseases scheduled during June 17-18, 2019 in Dubai, UAE provides a platform for research that gives new views into Microbiology, Molecular bacteriology and Virology, Clinical diagnostic methods of Virology and Bacteriology, Bacterial and Viral infections, Animal Bacteriology and Virology, Paediatric Virology, Human Bacteriology and Virology, Medical virology.
Bacteriology and Virology have progressively an important to human society. These are the most important branches of life sciences. As we know that microbes directly or indirectly affecting all the activities of our life like, food, clothing, shelter, health hygiene etc., microbiology has made vast progressive in all these fields to improve the quality of our life and for the betterment of our life. Infectious diseases are very much dangerous and have been conquered by new drugs, good quality of agricultural crops improved by using new techniques of genetic engineering and these are becoming possible only because of Microbiology.
In the new bio economy, Bacterial, Viral and Infectious disease play a very important role in representing major global challenges, upgrading waste streams to valuable food ingredients, counteracting life-style diseases and antibiotic resistance through the gut biota, making crop plants more resistance to extreme climatic change conditions, and functioning as host for the production of new biological drugs for treatments of diseases.
Why it’s in Dubai, UAE:
Bacterial, Viral and Infectious Diseases 2019 will be held in Dubai. Dubai is the largest and most populous city in the United Arab Emirates. On the southeast coast of the Persian Gulf, it is the capital of the Emirate of Dubai, one of the seven emirates that make up the country. Dubai is a global city and is a major business and transport hub of the Middle East. Dubai is situated on the Persian Gulf coast of the United Arab Emirates and is roughly at sea level. The emirate of Dubai shares borders with Abu Dhabi in the south, Sharjah in the northeast, and the Sultanate of Oman in the southeast.
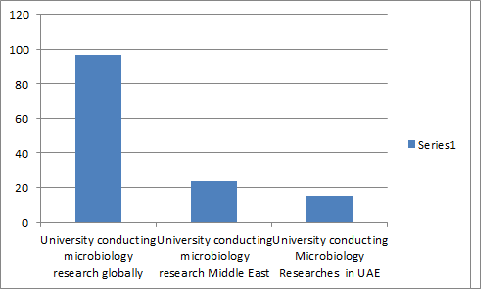
Major University doing Researches on Bacteriology and Virology in Middle East
- University of Exeter
- American University of Beirut
- King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals
- King Saud University
- King Abdul-Aziz University
- United Arab Emirates University
- Major University doing Researches on Bacteriology and Virology in UAE
- University of Sharjha
- United Arab Emirates University
- Abu Dhabi University
- Ajman University
Major University doing Researches on Bacteriology and Virology Globally:
- University of Tokyo, Japan
- Osaka University, Japan
- Harvard University, United states
- Kyoto University, Japan
- University of Adelaide, Australia
- University of oxford, United Kingdom
- Zhejiang University, China
- National university of Singapore, Singapore
- University of Chicago, United States
Major Bacteriology and Virology Researches centre globally:
- Centre for Emerging Viral Infections Research
- Hunter Medical Research Institute
- Centre for Global Research and Intervention in Infectious Diseases
- Infectious and Immunologic Diseases Research Centre
Major Bacteriology and Virology Research Centre Middle East:
- Qatar Biomedical Research Institute
- Molecular Biology and Genetics Lab
- Freiburg Medical Laboratory
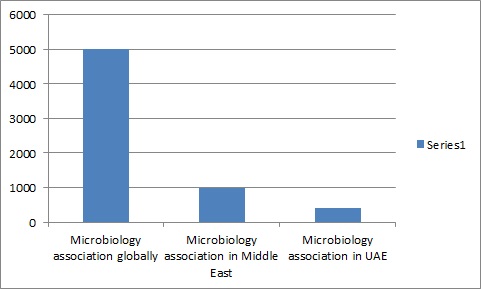
Major Bacteriology and Virology Associations Globally:
- International Union of Microbiological Societies
- British Infection Association
- International Retroviology Association
- North American Mycological Association
- Infectious and Immunologic Diseases Research Centre
- Global virus network
- HIV Medicine Association
Major Bacteriology and Virology Association around Middle East
- Pharmacy Organization
- Egyptian American Medical Association
- Coptic Medical Association
- The Journal of Egyptian Medical Association
Major Bacteriology and Virology Association in UAE
- Emirates Medical Association
- New York University, Abu Dhabi
- Masdar Institute
Major Bacteriology and Virology Societies Globally:
- International Union of Microbiological Societies
- Society for general Microbiology
- Federation of Infection Societies
- Canadian Society of Microbiologists
- Federation of European Microbiological Societies
- Pan-American Society for Clinical Virology
- European Society for Virology
- International AIDS Society
Major Bacteriology and Virology Societies around Middle East
- Asia- Pacific Society for Medical Virology
- European Society for Veterinary Virology
- Italian Society of Virology
- Hellenic Society for the Study of Prevention of AIDS
- Iranian Society of Microbiology
- Bacteriology Association and Societies
- Virology Association and Societies
Major Bacteriology and Virology Societies in UAE
- Saudi Society for Medical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (SSMMID)
- Hellenic Society for the Study & Prevention of AIDS
- Norwegian Society for Virology
- Danish Society for Virology
- Italian Society of Virology
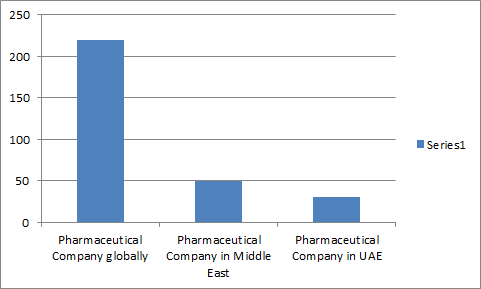
Global pharmaceutical industries manufacturing antimicrobial products
- Merck and Co
- Johnson and Johnson
- GlaxoSmithKline
- Bristol-Meyers Squibb
- Aventis
- Pharmacia
- Novartis
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche
- Astra Zeneca
- Abott Laboratories
- Wyeth
- Eli Lilly and Co
- Schering Plough
- Bayer
Pharmaceutical industries manufacturing antimicrobial products in Middle East
- Tabuk Pharmaceutical
- Bayer Middle East FZE
- CAD Middle East Pharmaceutical
- Genpharm Services
- Gilead Science Middle East Office
Pharmaceutical industries manufacturing antimicrobial products in UAE
- Neopharma
- Life Parma
- Modern Pharmaceutical Company
- Medisal Pharmaceutical Industry
Related conference
- 14th International Conference on Infectious Diseases, Prevention and Control March 21-22, 2019 Dubai, UAE
- World Conference on Vaccine and Immunology November 21-22, 2019 Dubai, UAE
- 11th Euro-Global Conference on Infectious Disease September 23-24, 2019 London, UK
- Annual Meeting on Infectious Diseases July 29-30, 2019 Amsterdam, Netherlands
- 15th World Congress on Endocrinology & Diabetes; September 19-20, 2019 Prague, Czech Republic
- 12th Edition of International Conference on Infectious Diseases, April 22 -23, 2019, Holiday Inn Rome Aurelia, Rome, Italy
- 3rd Global Summit of the Diabetes and Endocrinology (Diabetes-2019) ; May 30-31, 2019 at Nice, France
- 12th Annual Congress on Immunology & Immuno genetics October 21-22, 2019 Rome, Italy
- 11th Global Summit on Immunology and Cell Biology July 29-30, 2019 Sydney, Australia
Conference Highlights
- Bacteriology
- Virology
- Global Spread of Viruses
- Parasitology
- Neglected Tropical and Rare Infectious Diseases
- Advances in Antimicrobials, Vaccines and Therapeutics
- Clinical Microbiology & Virology
- Clinical Immunology
- Infectious Diseases Prevention, Control and Cure
- Epidemiology of Re-Emerging Infectious Diseases
- Causes, Symptoms and Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases
- Case Studies
- Infectious Diseases
- Bacterial and Viral Genomics
- Antiviral, Antibacterial, Antifungal Agents
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | June 17-18, 2019 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | Day 1 | Day 2 | |
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Bacteriology & Parasitology
- Journal of Infectious Diseases & Therapy
- Journal of Medical Microbiology & Diagnosis
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by